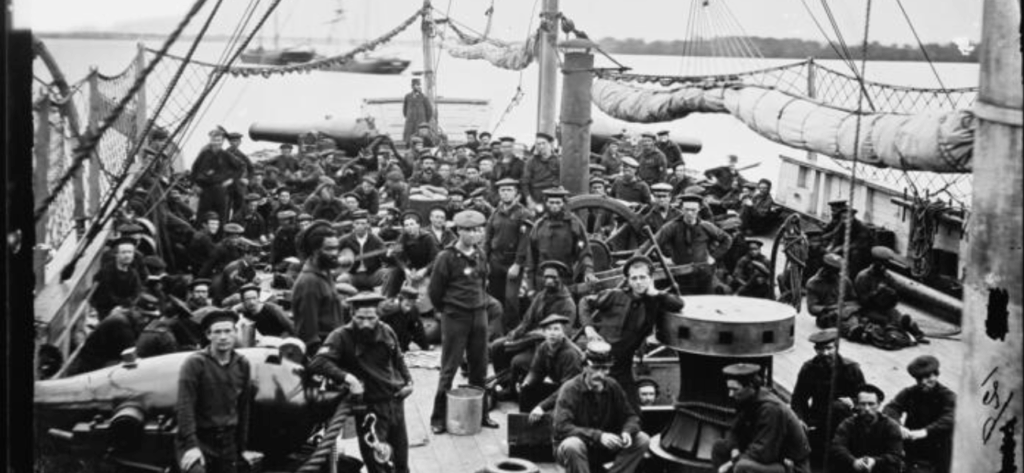
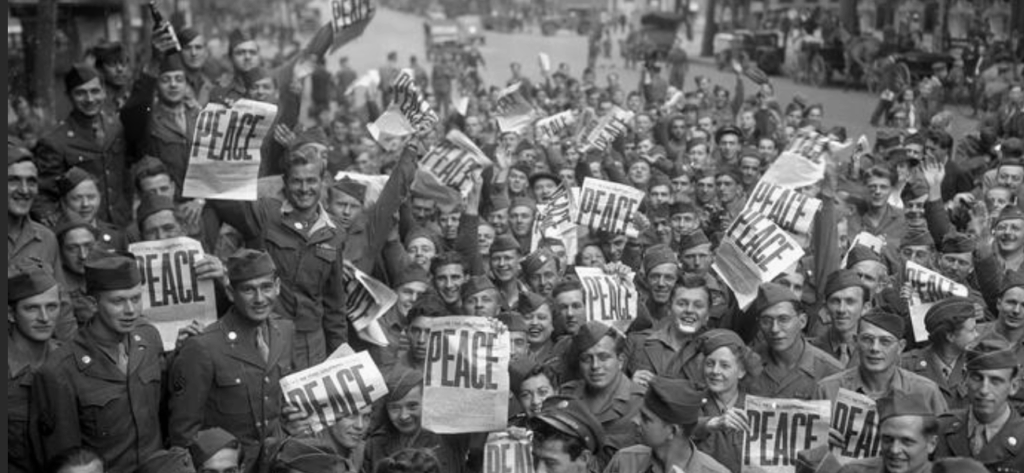
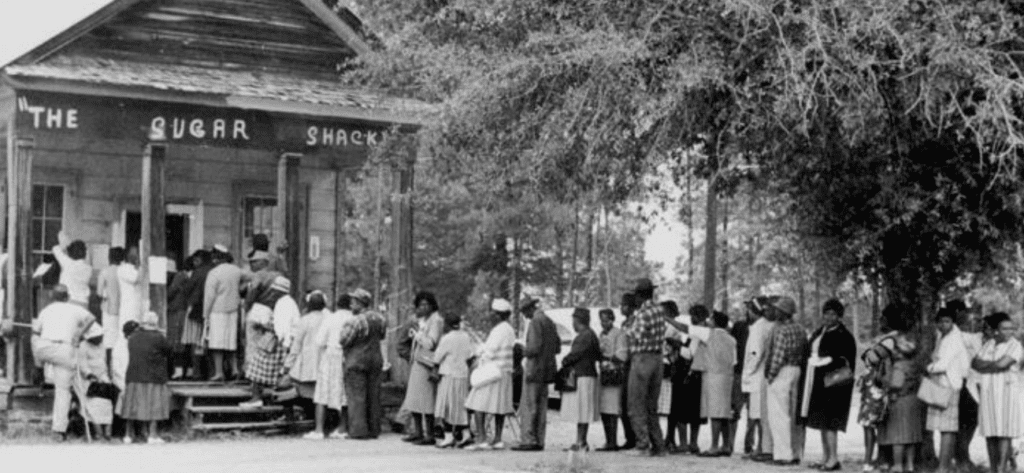
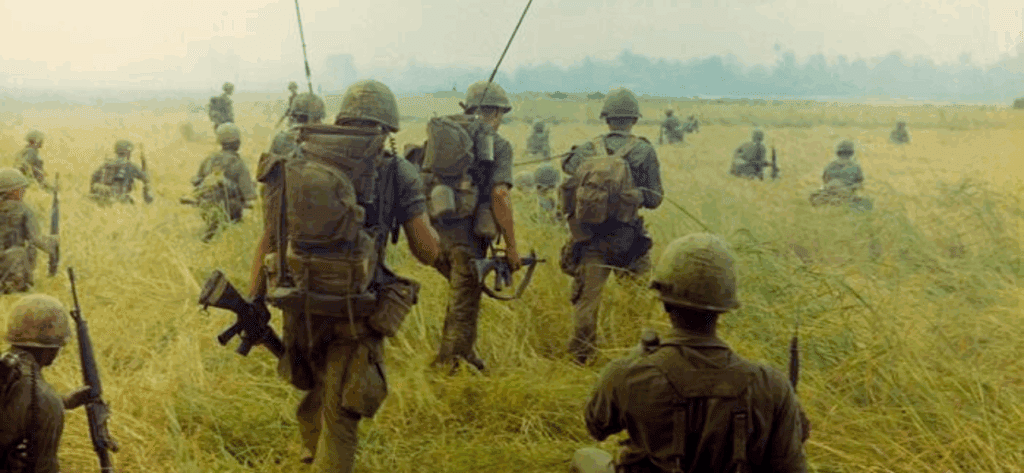
During the Revolutionary War, African Americans joined the Continental Army to obtain political freedom for the United States and their own freedom from slavery. Although some liberated themselves through military service, the institution of slavery remained intact. During the Civil War, thousands of African Americans joined the Union Army. These records testify to African Americans’ long tradition of military service.
Cato Greene—captured in Guinea, Africa, and sold into slavery in Rhode Island—fought in the Revolutionary War “to obtain his freedom.” Greene’s discharge papers record that he served in Rhode Island regiments for five years and was discharged from the Continental Army in 1783 by Gen. George Washington. Greene died in 1826 at the age of 86.
Pension affidavit submitted by Cato Greene, June 6, 1820.
National Archives, Department of Veterans Affairs
Discharge papers for Private Cato Greene, June 5, 1783.
National Archives, Department of Veterans Affairs
This document is being featured in conjunction with the National Archives’ National Conversation on Civil Rights and Individual Freedom. Click here to see more related records.
The “National Conversation on Rights and Justice” is presented in part by AT&T, Ford Foundation, Seedlings Foundation, and the National Archives Foundation.